Open Source AI with Alibaba Qwen
With Vlad, Head of AI Products and Solutions at Alibaba Cloud
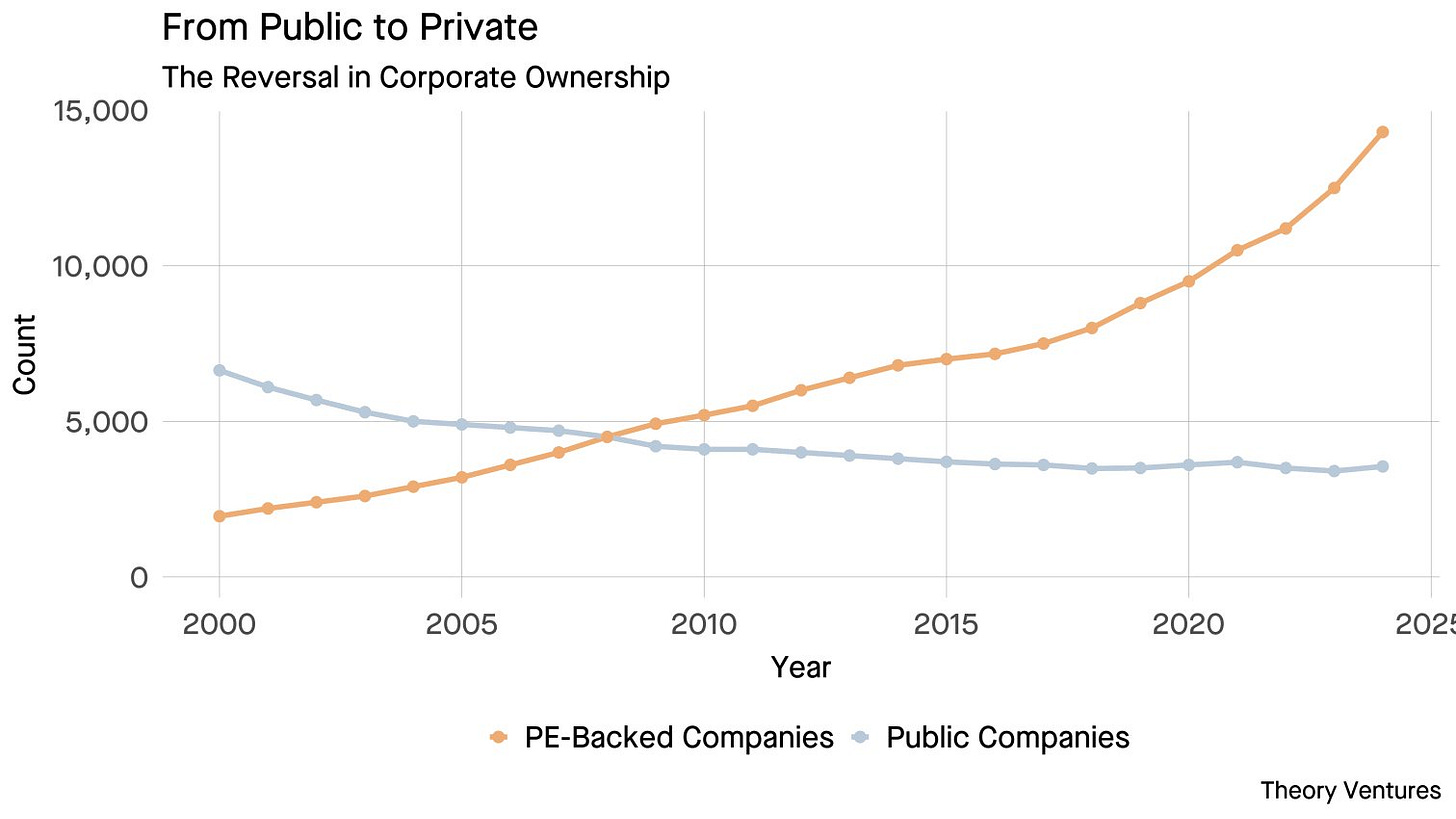
Software Synthesis analyses the evolution of software companies in the age of AI - from how they're built and scaled, to how they go to market and create enduring value. You can reach me at akash@earlybird.com.
Upcoming events in London
December 4th: Paper Club on RL and Multimodal Models
December 11th: AI Engineering with Cursor
December 15th: 2025 Reflections with Google and Earlybird AI Friends
Last week we hosted Vlad from Alibaba Cloud to discuss the Qwen model family, which are some of the most heavily used open source models.
Alibaba Cloud
Alibaba Cloud positions itself as one of the few public hyperscale cloud providers with a complete, vertically integrated AI stack. The company operates 92 data centres globally across 29 regions.
Current European presence includes five data centres (three in Frankfurt, two in London), with upcoming regions in France and Netherlands. The company was founded in 2009 as part of Alibaba Group’s IT team before becoming a standalone cloud business focused on “user first and AI driven” strategy.
Alibaba Cloud maintains its own homegrown technology stack from the operating system level up. This includes custom kernels, compute infrastructure, storage services, networking, and security layers.
The Qwen Model Family
Core Philosophy
Qwen represents Alibaba’s commitment to open source AI development under Apache 2.0 licensing, providing significant freedom for commercial use. The models are designed to balance performance with efficiency (reflecting the broader Chinese AI ecosystem’s adaptation to compute access).
Model Variants & Specifications
Text Models:
Dense models: 0.6B to 32B parameters
Mixture of Experts (MoE): Qwen3-30B-A3B 32B and Qwen3-235B-A22B (with 22B active at inference)
Qwen3-Max: flagship commercial model exceeding 1 trillion parameters
Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B: 8B parameter model with 3B active parameters
The variety in sizing allows developers to choose optimal performance-to-resource ratios for their specific use cases.
Multimodal Capabilities
Qwen3-VL (Vision-Language):
Supports 256,000 token context window for large video processing
Near real-time performance (5-second delay) for video analysis
Applications include video labeling, tagging, content moderation, quality management
Particularly strong with complex images like tables and diagrams
Qwen-Audio:
Speech recognition and audio processing
Pairs with VL model for comprehensive multimodal applications
Qwen-Omni:
Experimental single model for all modalities
Goal is eventual AGI-like architecture
Demonstrated in edge computing scenarios (mobile devices)
Qwen Coder:
Specialised for code generation
Trained on massive code base during second phase of model training
Engineers had to drop down to PTX (low-level instruction set) for optimization
Competitive with leading code models
Available across multiple IDEs
Reasoning & Thinking Models
Qwen initially released a hybrid reasoning/non-reasoning model but later separated them based on community feedback. Key innovation is the “thinking budget” feature that allows users to define token limits for reasoning. Once the budget expires, the model automatically switches to instruct mode, optimising GPU resource utilisation.
The flagship Qwen3-Max commercial model ranks competitively with OpenAI, Claude, and Google Gemini on major benchmarks, though the competitive landscape shifts rapidly with frequent releases.
Multilingual Support
Qwen3 supports 119 languages and dialects, making it effectively universal for global deployment. This represents a major breakthrough from Qwen2.5’s ~30 language support.
Generative AI: The Wan Family
The Wan family handles video and image generation with multilingual capabilities. Wan 2.2 is open source under Apache 2.0, while Wan 2.5 is commercial.
Capabilities:
Text-to-video, text-to-image
Image-to-video, video-to-video editing
Currently supports 15-second video generation
Performance comparable to Google Veo and Sora
Brand customisation for organisational alignment (colours, fonts, shapes)
Use Cases:
Social media content generation
Broadcasting and sports content
Corporate marketing materials
Commercial vs Open Source Distinctions
Development & Training
Commercial Models:
36 trillion tokens for general training
Continuous post-release tuning and updates
Enhanced security and content generation support
Extended context windows up to 1 million tokens
Access to caching and optimisation features
Open Source Models:
~20 trillion tokens (roughly 1.5x less than commercial)
Fixed at release date, no continuous updates
Context windows: 32K to 128K depending on configuration
Community-driven development and derivative models
Self-managed training and fine-tuning
Support & Pricing
Commercial:
Token-based pricing through Model Studio
Full technical support from Alibaba Cloud
Fine-tuning tools and evaluation models (in pilot, coming soon internationally)
Available in Singapore, Hong Kong;; Europe in 2026
Open Source:
Free to use and modify
Community support
Self-hosted with user-controlled infrastructure
Derivative models emerging (Japanese, Arabic language variants)
Technical Infrastructure & Deployment
Model Studio & Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Model Studio provides fully managed AI services combining:
Qwen family models (text, vision, audio)
Partner models (DeepSeek, Glm, Kimi, Llama, others)
Token-based consumption across multiple models
Agent orchestration capabilities
MCP native support
PAI (Platform for AI)
Elastic Algorithm Service enabling:
Few-click deployment of latest Qwen models on GPU infrastructure
GPU pool creation and load distribution
Fully managed infrastructure
Vector Database Options
Multiple managed services:
AnalyticDB for Postgres (with vector engine, built on Greenplum)
Hologres (MPP database with vector engine, homegrown product)
Elasticsearch and OpenSearch (managed services)
Milvus (fully managed)
Choice depends on use case: AnalyticDB works with larger data platforms (MaxCompute), Hologres optimised for specific workflows.
Agent Framework & Tools
Qwen Agent (Open Source):
Platform for agent orchestration
Supports planning, decision making, information management
Integration with various tools and functions
MCP-based tool selection and execution
Qwen Guard:
Enterprise guard-railing solution
Uses LLM to control input/output
Customisable policies with default integration
Protection against prompt injection and other attacks
Additional Tools:
Qwen3 Embedding and Reranker
Open source RAG framework
OCR capabilities (Qwen OCR for text-heavy documents)
Key Discussion Points & Insights
Adoption Patterns
The community shows fast adoption of Qwen open source models. Major platforms like HuggingFace integrated Qwen models into HuggingChat based on technical merit rather than advocacy. Companies like Airbnb have said that they use OpenAI for pilots but switch to open source models like Qwen for production due to cost efficiency at scale.
Derivative models demonstrate strong community engagement, particularly language-specific implementations (Japanese model topped charts for extended periods, Arabic implementations showing strong performance).
Performance & Optimisation
Performance varies significantly across hosting solutions. Alibaba Cloud uses its custom acceleration technology (PAI-Lingjun) but doesn’t test Qwen performance on competitors like Google Cloud or AWS. Each cloud provider applies different optimisations and accelerations, making direct comparisons difficult.
Cost Economics
The token-based pricing for commercial models can become expensive at scale, driving production workloads toward open source alternatives. The calculation of when self-hosting becomes more economical than API calls depends heavily on specific use cases and scale. Alibaba Cloud offers both Model Studio (token-based) and PAI (AI infrastructure-based) to provide flexibility.
Fine-Tuning Strategy
Fine-tuning capabilities are being piloted within Alibaba Cloud Model studio in some regions. The recommended approach follows standard best practices:
Start with system prompts
Try LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation)
Full fine-tuning only if necessary (requires significant engineering expertise)
Fine-tuning isn’t always necessary for solving specific problems, and over-reliance on it can indicate other issues with the implementation.
Future Roadmap & Technical Forecasts
Context Length Evolution
Current: Up to 1 million tokens (commercial)
Forecast: 10 million to 100 million tokens
Challenge: Processing massive documents while maintaining attention across entire context
Model Architecture Questions
The engineering team forecasts several architectural considerations:
All-modality convergence toward single universal models
Potential limitations of transformer architecture at current scaling
Focus on test-time compute scaling
Data scaling and quality improvements
Enhanced reinforcement learning implementation
Some experts suggest the industry may have reached transformer architecture limitations, requiring new approaches beyond simply increasing model size.
Open Source Strategy
Alibaba remains committed to releasing both commercial and open source versions of new models. This dual approach serves multiple purposes:
Developer community engagement and ecosystem building
Direct user feedback for rapid iteration
Path to commercial model adoption
Competitive differentiation in a crowded market
The Qwen2.5 Math and Qwen2.5 Coder models extensively generated synthetic training data that fed back into pretraining for subsequent versions, creating a virtuous cycle of improvement.
Competitive Context & Market Position
Chinese AI Ecosystem
The broader Chinese AI landscape features intense competition. Following DeepSeek’s breakthrough, major tech companies (Alibaba, Baidu, Moonshot, others) significantly accelerated foundation model investments. DeepSeek pioneered many efficiency innovations but hasn’t maintained momentum recently. Moonshot’s Kimi briefly overtook Qwen on some leaderboards.
Qwen models remain among the most popular open source options globally, with MetaLM showing strong consumption across various API reselling platforms. The competitive intensity means new model versions release constantly, making benchmarks quickly outdated.
Vertical Integration Advantage
Alibaba’s control of models, and cloud infrastructure represents a rare combination. Most competitors lack global cloud presence. This vertical integration enables:
Full optimisation across the stack
Better cost control for model training
Custom acceleration technologies
Faster iteration and deployment
Strategic Implications
Open Source as Go-to-Market
Alibaba’s open source strategy serves multiple strategic purposes:
Developer mindshare and ecosystem development
Rapid feedback loops for model improvement
Lower barrier to experimentation leading to commercial adoption
Competitive differentiation against closed-source-only competitors
The community’s willingness to create derivative models (Japanese, Arabic variants) validates technical quality while expanding Qwen’s reach into specialized domains and languages.
Build vs Buy Dynamics
For enterprises, the decision calculus involves:
API services: Fast to start, expensive at scale, less control
Self-hosted open source: Higher upfront engineering cost, better long-term economics at scale, full control
Managed services: Middle ground with varying levels of optimization
The emergence of companies like Fireworks and Together.ai suggests a sustainable market for managed open source model hosting, capturing value from optimization and operations.
Data & Synthetic Training
The use of Qwen2.5 models to generate synthetic training data for Qwen3 hints at an important trend: models improving through self-generated data. This approach requires careful quality control but can overcome data scarcity constraints, particularly relevant given export restrictions and data access challenges.
Q&A
Downstream RL Training
One attendee noted Qwen3 serves as an excellent seed model for downstream reinforcement learning training and domain specialization. However, reward hacking occurs during RL training. Alibaba expressed interest in collecting specific feedback to bring back to engineering teams for future model development.
Computer Use Agents
When asked about computer use capabilities (similar to Lovable or v0), Vlad clarified that Qwen Agent framework provides orchestration tools, but interactive computer control features might be product-level additions to Qwen Chat rather than core model capabilities. This mirrors how ChatGPT’s Operator exists as a product feature rather than model capability.
Voice Capabilities
Alibaba offers cascaded voice models (ASR and TTS) but attendees noted the industry trend toward native voice-to-voice models for better latency and naturalness. While cascaded models currently offer better reliability for enterprise use cases requiring tool calling and reasoning, native voice-to-voice models will likely improve significantly in the coming months for consumer applications.
Prompting Challenges
A significant practical concern raised: switching from one model to another (e.g., Gemini to Qwen) requires substantial prompt engineering adjustments. While competitors like Anthropic provide detailed migration guides explaining how to adjust prompts between model versions, Qwen’s documentation lacks comprehensive prompting guides, especially for cross-model migration.
Signals
What I’m Reading
Moats Before (Gross) Margins: Revisited
Earnings Commentary
Most accelerators without CUDA and NVIDIA’s time-tested and versatile architecture became obsolete within a few years as model technologies evolve. Thanks to CUDA, the A100 GPUs we shipped 6 years ago are still running at full utilization today, powered by vastly improved software stack.
Jensen Huang, Nvidia Q3 2026 Earnings Call
All of the latest GPUs that are running are running at full capacity and not just them, the last generation GPUs, even GPUs from 3 to 5 years ago, so also several generations back, those GPUs are to this day still running at full capacity.
Yongming Wu, Alibaba Q2 2026 Earnings Call
Have any feedback? Email me at akash@earlybird.com.